Ms Zuha Tiwana is a psychologist, freelancer, and analyst. She can be reached at [email protected]
The Geopolitical importance of Ukraine for Russia
Russia’s endless interest in Ukraine and its conflict with it have many historic and geopolitical reasons. Kiev, the capital city of Ukraine, was the birthplace of Russia as a state back in the 9th century. Ever since the USSR was dissolved, Russia lost the Baltic states to the European Union (EU) which also impacted the Russian hegemony among the Balkans.
Most of the Russians left in Ukraine and Moscow feel that it is very important to keep Ukraine from conceding to the Western powers. Whenever Russia feels threatened, Putin uses aggressive policy to stop what it doesn’t want.
Ukraine has been very important for Russia due to its geography which links the latter to Eastern Europe. It acts as a buffer state. If Ukraine joins the European Union, Russia will become weaker on the western front. Therefore, in order to prevent the risks to the national interests of Russia, it appears to be planning a Ukrainian invasion.
The Rise of the Ukrainian Crisis
In November 2013, the people of Ukraine protested against then-President Viktor Yanukovych, on his decision for no economic cooperation with the European Union. He rejected a deal of economic integration with the EU. As a result, the capital city, Kiev, became full of angry people on roads and the situation worsened with every passing day. On retaliation by the state, the number of protestors increased further and the situation got out of control. The President fled Ukraine in February 2014.
Russia occupied Crimea in March 2014 which increased the ethnic issues in Ukraine. As a result, the Russian separatists in Donetsk and Luhansk regions proclaimed independence from Ukraine through a referendum. The violence resulted in the killing of more than 10,300 people in April 2014.
Russia’s government denied any involvement in the violence and conflict in Ukraine but the US and the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) reported a large number of Russian troops and equipment near the border. The violence transitioned into an international crisis when in July, a Malaysian flight was shot down in the Ukrainian airspace, killing almost three hundred people on board. The reports showed that a Russian-built air missile was involved in the attack.
The Minsk Accords were brought in by Germany, Russia, France, and Ukraine to cease the violence, but they remained unsuccessful. The agreement comprised withdrawal of weapons, ceasefire, and Ukrainian control over the land. The Minsk Accords 2015 were a complete failure.
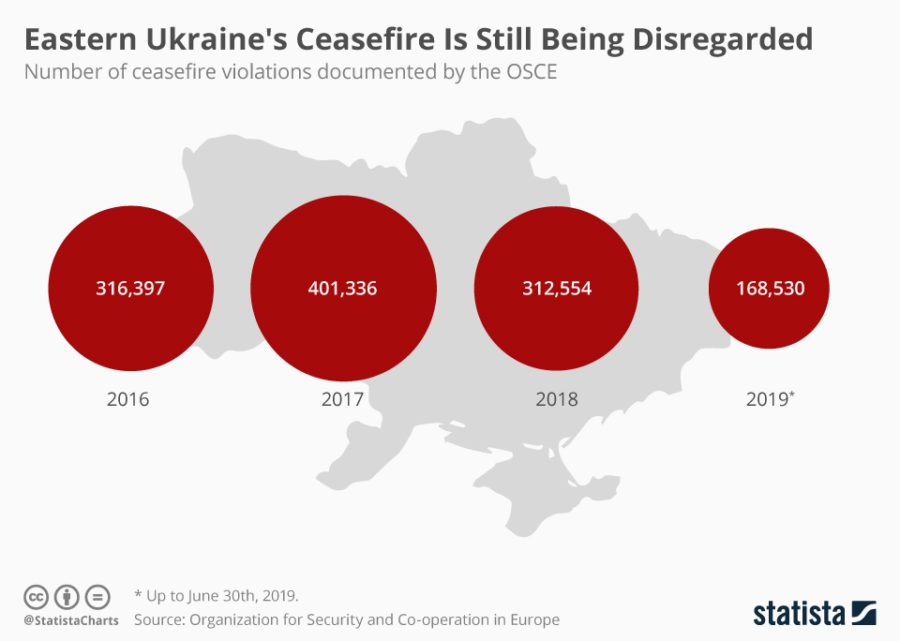
Cyber Attacks on Ukraine
Ever since the start of Russia’s conflict with Ukraine, the latter has been under different cyber attacks. In 2014, a loss of power was seen as a result of an attack. In 2015, a power blackout in a Ukrainian utility company happened. In 2017, the NotPetva cyber attack hit the computer systems in Ukraine. The attack has been attributed to Moscow, resulting in damage of billions of dollars.
Trump’s government helped Ukraine a lot with an increase in sanctions on Russia. In 2018, the US started weapons sales to Ukraine and imposed sanctions on twenty-one Russian officials and nine companies who contributed to the conflict. In September 2018, Russia held its military exercises and as a result, Ukraine joined the seven members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) and the United States in air exercises in western Ukraine.
Russia-Ukraine Conflict at Present
Russia’s conflict with Ukraine started back in 2014 and reached a stalemate in later years with few regular challenges and firing exchanges. Most recently, in 2021, an increase in violence has been seen in the Ukrainian land. The Russia-Ukraine conflict worsened when Moscow moved its military forces and weapons near the border it shared with Ukraine in October 2021, escalating the fear and chances of invasion among the Ukrainians.
The weapons brought in by Russia included missiles, armor, and other heavy equipment without any written warning or explanation by the Russian government. Satellite imagery and social media content from November and December 2021 has clearly shown the Russian equipment present near the border.
In December, the number of troops near the border reached around a hundred thousand. In this situation, the West looked quite concerned. The intelligence reports and offices in the United States started alleging Russia of its potential planning of occupying Ukraine by the start of 2022. The warning of invasion was very clear from the US intelligence officials. However, in mid-December, Russia came up with its demands for the Ukraine government.
Russian foreign office issued several demands including a ban on Ukraine to join the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). In addition, it also demanded a reduction in the number of NATO troops from Eastern Europe. This would eventually let Russia withdraw its troops from that area.
The steaming issues between Russia and US got escalated afterward. The US and all the NATO members strongly rejected all the demands of the Russian foreign office and threatened Russia with economic sanctions and repercussions if any military activity is initiated. Moreover, the US assured full Ukrainian support with small arms and weapons for retaliation if anything happens on the border.
United Nations Security Council held a session on 31st January 2022, which turned out to be a steamy and angry debate on the Russia-Ukraine conflict. The Russian troops around the Ukrainian border have become a global issue now. The continuous accusations of Russia and the US are very obvious. While Russia has accused the US of “whipping up hysteria” and repeatedly denied its plan of a Ukrainian invasion, the United States has blamed Russia for all the violence on the Ukrainian land.
Amidst the clash between the United States and Russia, the Ukrainian president, Volodymyr Zelensky, is looking forward to the sanctions to be put on Russia by the US and other NATO allies, before the Russian invasion of his land. More than 127,000 troops have been deployed by Russia on the border with Ukraine.
The West wants Russia to withdraw its troops and equipment from the border while Russia wants NATO to cease its operations in central and eastern parts of Europe. Russia also wants Ukraine to not be a part of the Western alliance for its borders to be secure in the future.
The Future Apprehensions
The already poor relations between Washington and Moscow are at risk of further decline as Russia’s conflict with Ukraine continues. Russian involvement in the Ukrainian land has caused global concern. NATO allies and the United States are ready to solicit a response on every action of Russia. The Russia-Ukraine conflict has impacted Russian relations with the United States, the European Union and also harmed its role in the solution of the Syrian civil war.
In the present scenario, if conflict sustains and NATO imposes new sanctions on Russia, the latter might retaliate by cutting off natural gas supplies to Europe. It will eventually cause a global inflation crisis. The world is already managing a downsized economy because of the pandemic and in this situation, the European economy is the most vulnerable.
According to BCA strategists, if Russia cuts gas to Ukraine, it will eventually stop Germany’s 18 percent imports, 77 percent of Hungary’s purchase, and a 38 percent import loss for Italy. Similarly, if Europe retaliates by imposing sanctions, Russia and Belarus will come together to harm 20 percent of Europe’s imports and 60 percent of Germany’s imports.
While Biden’s government has been throwing accusations at Putin, Chinese President Xi Jinping has shaken hands with the latter and called for NATO to not admit new members in the organization. In the ongoing Beijing Olympics, Vladimir Putin has been invited as a chief guest. The United States and its Western allies have announced a boycott of the Olympics, considering the Chinese atrocities in Uighur and Hong Kong. Russia, on the other hand, is holding China’s hands to have its support in the future against the Western foes.
If you want to submit your articles, research papers, and book reviews, please check the Submissions page.
The views and opinions expressed in this article/paper are the author’s own and do not necessarily reflect the editorial position of Paradigm Shift.



















